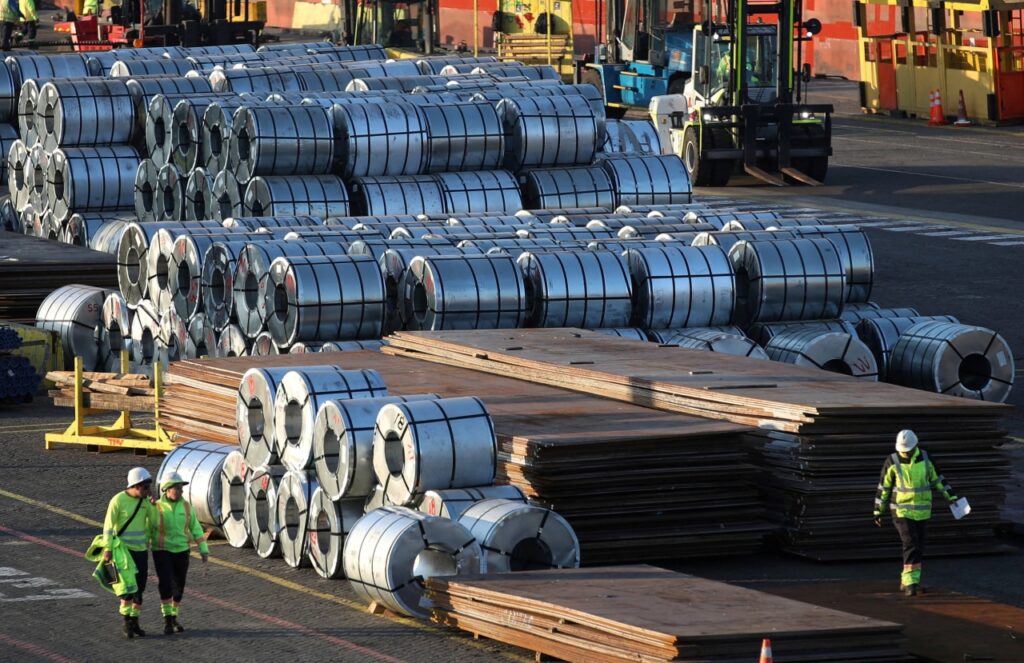
China announced that starting on January 1, 2024, exporters will be required to secure permission before shipping specific steel products. This significant regulatory change aims to manage the country’s steel output and ensure compliance with environmental standards while addressing domestic market needs.
The Ministry of Commerce in China stated that these controls are part of a broader strategy to reduce overcapacity in the steel sector. Officials emphasized that the measures are designed to enhance the quality of steel exports and promote sustainable production practices. As a result, exporters will need to apply for licenses, a move that could impact both domestic producers and international buyers.
Impact on Global Steel Market
Industry analysts expect these export controls to have a substantial effect on the global steel market. China is the world’s largest steel producer, contributing over 50% of global output. By implementing these restrictions, the nation aims to stabilize local prices, which have fluctuated due to excessive supply and competition.
The new policy could lead to increased prices for steel products internationally as supply tightens. Experts predict that countries reliant on Chinese steel may need to seek alternative suppliers, which could disrupt existing trade relationships. Additionally, the requirement for export licenses may create delays in shipments, affecting production timelines for manufacturers worldwide.
The Chinese government has indicated that the export controls will not apply to all steel products. Specific categories will be determined, and exporters will need to monitor updates from relevant authorities to ensure compliance. This approach allows China to selectively manage its steel exports while still fulfilling international demand for certain products.
Reactions from the Industry
Reactions to the announcement have been mixed. Some industry leaders view the export controls as a necessary step toward ensuring environmental sustainability. They argue that by regulating exports, China can maintain better control over its steel production processes, ultimately benefiting the global market in the long run.
Conversely, other stakeholders express concern about the potential negative impacts on international trade. Trade associations representing steel importers have voiced worries about increased costs and supply chain disruptions. The situation may lead to heightened tensions in trade negotiations, particularly with countries heavily dependent on Chinese steel.
The Chinese government has reiterated its commitment to balancing domestic needs with international obligations. As the steel industry continues to evolve, stakeholders will be closely monitoring how these export controls influence global markets and trade dynamics.
This development marks a pivotal moment for the steel industry, reflecting China’s focus on sustainable growth and regulatory oversight. How the market adapts to these changes remains to be seen, but the implications are expected to resonate across various sectors globally.