BREAKING NEWS: A game-changing tool for Linux users has just launched, bringing a vital system restore feature akin to macOS’s Time Machine. Timeshift is now available, providing Linux users with the ability to create system snapshots and easily recover from potential system failures.
This innovative tool addresses a significant gap in the Linux ecosystem, where users lacked a reliable safety net for system restores. Timeshift allows users to roll back their operating systems to previous states, making it easier to experiment with new kernels, distributions, or updates without the fear of losing critical system configurations.
Why it matters NOW: With the growing popularity of Linux, especially among developers and tech enthusiasts, Timeshift offers peace of mind. Users can confidently explore new features or settings, knowing they have a fail-safe option in case of errors. This is crucial for both novice users and seasoned professionals who rely on their systems for productivity.
Timeshift simplifies the installation process, supporting major Linux distributions including Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Debian, and Arch. Users can install it via a single command, provided their systems meet the prerequisites. The installation is rapid, taking only seconds, and once set up, Timeshift begins creating snapshots automatically based on user-defined schedules.
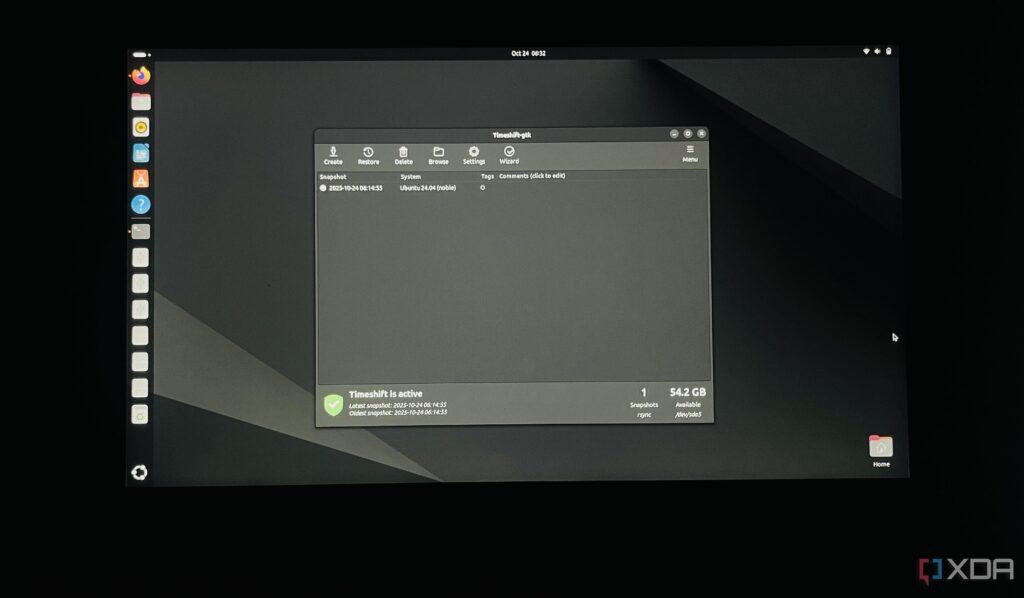
How to use Timeshift: After installation, users can launch Timeshift from the app menu or terminal with the command sudo timeshift-gtk. The tool prompts users to select a snapshot type—either RSYNC or BTRFS. RSYNC is the default option, suitable for all file types. Users can choose where to save snapshots, either on external drives or internal partitions with ample space.
Timeshift enhances user experience with features like automatic snapshots, incremental backups, and the ability to restore systems even from the GRUB boot menu. This flexibility makes it an essential tool for anyone frequently testing or modifying their Linux environments.
However, users should note that Timeshift does not back up personal files by default; it focuses solely on system-level files. This means that while Timeshift can recover operating systems, users must use a separate backup solution for personal data. Additionally, users should manage their storage carefully, as snapshots can accumulate and consume significant disk space over time.
For those experimenting with different Linux distributions, Timeshift offers cross-distribution restore capabilities. Users can easily switch between distros like Ubuntu, Xubuntu, and Linux Mint, restoring their systems to previous states without complications.
In summary, Timeshift emerges as a crucial tool for Linux users, enhancing system stability and user confidence in exploring new software and configurations. With its official launch in October 2023, now is the perfect time for Linux enthusiasts to integrate Timeshift into their systems.
As this tool gains traction, users are encouraged to share their experiences, ensuring that others can benefit from the newfound security it provides. With Timeshift, Linux users can finally embrace the freedom to experiment without fear.





