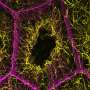
Researchers have discovered that water molecules can significantly alter the structure of prolinol, a molecule commonly used as both a catalyst and a building block in chemical synthesis. This finding, detailed in a study published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, sheds light on the dynamic interactions between water and chiral catalysts.
The study focused on the hydration process of prolinol, revealing that even a small number of water molecules can completely change its preferred structural form. This insight highlights the importance of considering solvent interactions in catalytic reactions, which could lead to advancements in the efficiency of chemical processes.
Significance of the Findings
Prolinol is known for its role in various chemical reactions, particularly in asymmetric synthesis, where it helps create molecules with specific chiral properties. Understanding how water molecules influence prolinol’s structure may open new avenues for improving reaction conditions and yields in both academic and industrial settings.
The research team meticulously analyzed the stepwise hydration of prolinol. They found that as water molecules attach to the prolinol structure, they induce a series of conformational changes. These changes can result in different catalytic behaviors and efficiencies, underscoring the complexity of molecular interactions in chemical reactions.
Implications for Future Research
The findings of this study may have broader implications for the field of chemistry. By understanding the role of solvent molecules, chemists can design better catalysts that respond dynamically to their environment. This research not only advances the scientific understanding of prolinol but also contributes to the development of more sustainable and efficient chemical processes.
As the study reveals new insights into the relationship between water and prolinol, it emphasizes the need for further exploration of solvent effects in catalysis. Future research could build on these findings to enhance the design and application of chiral catalysts, ultimately leading to more effective methodologies in chemical synthesis.
In conclusion, the interaction between water molecules and prolinol represents a significant step forward in the understanding of chiral catalysts. This research not only enhances our knowledge of molecular behavior but also paves the way for future innovations in chemical synthesis and catalysis.