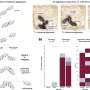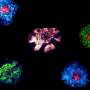
Research has unveiled a significant mechanism by which T cell receptors (TCRs) evade endocytosis, a process that often disrupts immune responses. A study conducted at the Laboratory of Dr. Emily Chen and published in Nature Immunology on October 15, 2023, highlights the role of actin wavefronts in preserving TCRs during immune activation, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of T cells in fighting infections.
When the body encounters pathogens, it activates the adaptive immune system, with T cells serving as key players in this defense. These cells actively monitor their environment for signs of infection and initiate responses to eliminate the invading agents. The dynamic nature of T cells allows them to alter their structure and composition upon interacting with infected cells, which is crucial for their function.
Understanding T Cell Dynamics
T cells possess the ability to rapidly reorganize their cellular components, a process essential for their immune functions. The recent study focuses on how actin, a structural protein, contributes to this dynamic capability. Researchers found that actin wavefronts form at the T cell membrane during interactions with target cells. These wavefronts help stabilize TCRs, preventing their premature internalization through endocytosis.
Endocytosis can hinder the immune response by reducing the number of available TCRs on the cell surface. By utilizing actin wavefronts, T cells can maintain a higher density of TCRs, enhancing their sensitivity and responsiveness to pathogens. This mechanism underscores the complexity of T cell activation and the intricacies of immune signaling.
Implications for Immunotherapy
The findings from this research have significant implications for immunotherapy, especially in the context of cancer treatment and vaccine development. Understanding how TCRs are preserved could lead to enhanced strategies for improving T cell responses against tumors and infectious diseases. The study suggests that manipulating actin dynamics might optimize T cell functionality in therapeutic settings.
In summary, the study sheds light on the critical role of actin wavefronts in T cell receptor dynamics, offering new insights into immune system function. As researchers continue to explore these mechanisms, the potential for developing innovative immunotherapies grows, paving the way for more effective treatments in the fight against various diseases.