Research on the bacterium Acinetobacter baumannii has unveiled critical mechanisms behind bacterial drug resistance, a pressing issue in healthcare. This species, notorious in hospitals across the United States, accounts for infections in over 1% of hospitalized patients. The findings, published in September 2023, shed light on how A. baumannii adapts and survives in environments saturated with antibiotics.
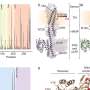
The study, conducted by scientists at the University of California, San Diego and funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), utilized experimental evolution techniques. Researchers observed how A. baumannii evolves in real-time by exposing it to various antibiotics. The bacteria displayed rapid genetic changes that enabled them to develop resistance, raising concerns about treatment efficacy.
Understanding the genetic mechanisms that facilitate this resistance is vital. The research team discovered that specific mutations in the bacterial genome contributed significantly to enhanced survival rates against antibiotic treatments. This adaptability poses a challenge for medical professionals, as A. baumannii infections can lead to severe complications, especially in immunocompromised patients.
In the course of the study, researchers noted that A. baumannii could not only survive but thrive under antibiotic pressure. The bacteria’s flexibility allows for swift genetic alterations, which can render previously effective treatments useless. This evolution underlines the need for new therapeutic strategies that can outpace the bacteria’s rapid adaptation.
The implications of these findings extend beyond individual treatment plans. The research highlights the necessity for hospitals to employ more stringent infection control measures and to review antibiotic stewardship practices. As drug-resistant infections become more prevalent, understanding the evolutionary pathways of bacteria like A. baumannii is crucial for public health efforts.
In conclusion, the investigation into A. baumannii provides a stark reminder of the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance in healthcare settings. As the research unfolds, it underscores the importance of continued surveillance and innovation in treatment approaches to combat these resilient pathogens effectively.






