Researchers from Zhejiang University and Shanghai Hexin Industrial Software Co., Ltd. have developed a new algorithm aimed at improving power analysis in digital integrated circuits (ICs). Their study, titled “Algorithm and evaluation of generating pseudo-datasets for integrated circuit power analysis,” addresses the increasing demand for extensive datasets necessary for machine learning applications within the electronic design automation (EDA) field.
The significance of accurate average power analysis in large-scale IC design cannot be overstated. Traditional datasets often fall short in both quantity and specificity, creating barriers for effective machine learning integration. Furthermore, accessing industrial data typically involves complex legal constraints, making it difficult for researchers and engineers to obtain the necessary information.
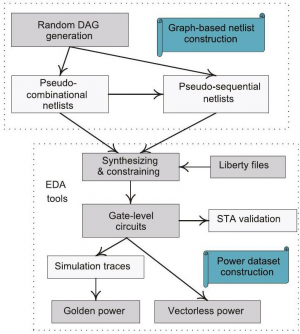
Innovative Approach to Data Generation
The research team has introduced a novel pseudo-circuit generation algorithm that leverages graph topology. Initially, the algorithm converts randomly generated directed acyclic graphs (DAGs) into gate-level Verilog pseudo-combinational circuit netlists. This process enables the efficient production of a substantial number of power analysis examples.
To enhance the utility of these datasets, the team incorporates register units that transform the pseudo-combinational netlists into pseudo-sequential circuit netlists. By adjusting hyperparameters, the algorithm allows for control over circuit topology, while appropriate sequential constraints are applied during synthesis to generate a comprehensive pseudo-circuit dataset. This innovative approach significantly increases the volume and variety of data available for analysis.
Evaluation and Results
The efficacy of the proposed algorithm was evaluated using mainstream power analysis software. Pre-layout average power tests were conducted on the generated circuits, comparing their performance against established benchmark datasets. The results confirmed the effectiveness of the dataset and underscored the operational efficiency and robustness of the algorithm.
“The generated pseudo-datasets show consistent power consumption distribution trends with benchmark datasets when tested with tools like Synopsys PrimeTime PX and Cadence Voltus,” said Zejia Lyu, one of the study’s authors.
Specifically, the study produced 1,000 sets of combinational and 1,000 sets of sequential circuit netlists. The algorithm also allows for the parallel generation of samples, effectively reducing time overhead associated with data production. Additionally, the sequential circuit generation factor α can be adjusted to address the zero-value phenomenon in sequential circuit power analysis, enhancing the dataset’s overall relevance.
The findings from this study highlight a significant advancement in the field of IC power analysis, providing a valuable resource for researchers and engineers alike. By overcoming existing data limitations, this research not only contributes to the academic community but also has practical implications for the development of future electronic devices.
The full text of the paper is available at: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.2400677.







