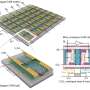
Recent innovations in memory technology are set to transform edge artificial intelligence (AI) applications. Researchers have developed atom-thin, content-addressable memory that significantly enhances the speed and efficiency of data processing. This breakthrough addresses critical limitations of current hardware, which often struggles with energy consumption and processing delays when moving data between internal memory components and processors.
The new memory technology is based on quantum dot structures, allowing for faster data retrieval and reduced energy requirements. Traditional data handling methods involve frequent transfers between memory and processing units, which can slow performance and increase power demands. By integrating this advanced memory directly into AI hardware, developers anticipate a marked improvement in responsiveness and operational efficiency.
Implications for Edge AI Applications
These advancements hold considerable promise for a range of edge AI applications, such as autonomous vehicles, smart home devices, and real-time data analytics. The ability to process data more efficiently at the edge—where data is generated—means that devices can perform tasks more rapidly and with less reliance on centralized cloud computing. According to industry experts, this shift could lead to a new era of AI deployment, characterized by enhanced capabilities and reduced operational costs.
Moreover, the adoption of this atom-thin memory technology could facilitate the development of more sophisticated AI models. As AI systems become more complex, the demand for efficient data management will grow. The innovative memory solution not only meets this requirement but also sets the stage for future advancements in AI hardware.
Energy Efficiency and Performance
Energy efficiency remains a critical concern in technology development, especially given the increasing global focus on sustainability. The newly developed memory technology promises to reduce energy consumption significantly. Traditional AI models can be power-intensive, often requiring substantial energy resources to function effectively. By minimizing the energy needed for data transfers, this new approach could contribute to greener AI solutions.
In practical terms, this means that devices powered by this memory technology can operate longer on battery power and generate less heat, leading to improved longevity and reliability. This aligns with the growing demand for eco-friendly technology solutions across various sectors.
The research team behind this breakthrough emphasizes the impact on industries ranging from telecommunications to healthcare. With faster, more efficient data processing capabilities, sectors that rely heavily on real-time data analysis stand to benefit immensely. The integration of this memory technology could lead to advancements in medical diagnostics, predictive maintenance in manufacturing, and enhanced user experiences in consumer electronics.
As the landscape of AI continues to evolve, the introduction of atom-thin, content-addressable memory marks a pivotal moment in the ongoing quest for faster and more efficient technology. With these advancements, the future of edge AI applications looks promising, heralding a new chapter in the intersection of hardware and artificial intelligence.







