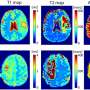
A groundbreaking study from researchers at York University has unveiled a novel artificial intelligence (AI) method that significantly improves the differentiation between progressive brain tumors and radiation necrosis on advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This advancement, reported in a recent publication from the Lassonde School of Engineering, could enhance clinical decision-making and treatment strategies for patients dealing with complex brain conditions.
The challenge of distinguishing between brain tumors and the necrosis that can occur following targeted radiation treatment poses a significant hurdle for medical professionals. Traditional MRI techniques often fail to provide clear differentiation, leading to potential misdiagnosis and inappropriate treatment plans. The new AI-based approach, developed under the guidance of a lead professor at York University, promises to offer a more reliable diagnostic tool.
AI Technology Revolutionizes Diagnosis
The AI system leverages advanced algorithms to analyze MRI scans with a level of precision that surpasses human capability. According to the study, early tests indicate that this method can improve diagnostic accuracy substantially, thus aiding physicians in making more informed decisions regarding patient care. The ability to reliably identify whether a lesion is a tumor or necrosis can directly impact treatment pathways and outcomes for patients, potentially reducing unnecessary procedures or treatments.
This innovative technique harnesses a vast dataset of previously diagnosed cases, allowing the AI to learn and adapt in ways that traditional diagnostic methods cannot. By employing machine learning, the system becomes increasingly adept at recognizing subtle differences between lesions, leading to a clearer understanding of the underlying health issues.
Implications for Clinical Practice
The implications of this research are profound. With brain tumors affecting countless individuals worldwide, the need for precise diagnostic tools is critical. The ability to accurately distinguish lesions could not only improve patient outcomes but also streamline healthcare processes, ultimately leading to cost savings in treatment and management.
As healthcare systems continue to embrace technological advancements, the integration of AI into diagnostic practices is becoming increasingly prevalent. The findings from this study not only highlight the potential of AI in radiology but also set a precedent for future research in medical imaging technologies.
The research team at York University is optimistic about the future applications of their findings. They believe that as AI technology continues to evolve, it will become an indispensable part of diagnostic and treatment protocols in various medical fields. The full details of the study are expected to be made available in the coming weeks, allowing for further scrutiny and discussion within the medical community.
In summary, the new AI technique developed at York University represents a significant leap forward in the field of neuro-oncology. By enhancing the ability to differentiate between brain tumors and radiation necrosis, this innovation holds promise for improving patient care and outcomes, marking an important step in the integration of AI into healthcare.