This week, significant advancements in our understanding of both ancient civilizations and animal behaviors were reported, ranging from Neanderthal fire usage to the surprising cooperation between killer whales and dolphins. These discoveries not only enhance our knowledge of human evolution but also shed light on the complexities of animal interactions.
Neanderthals and Fire: A Revised Timeline
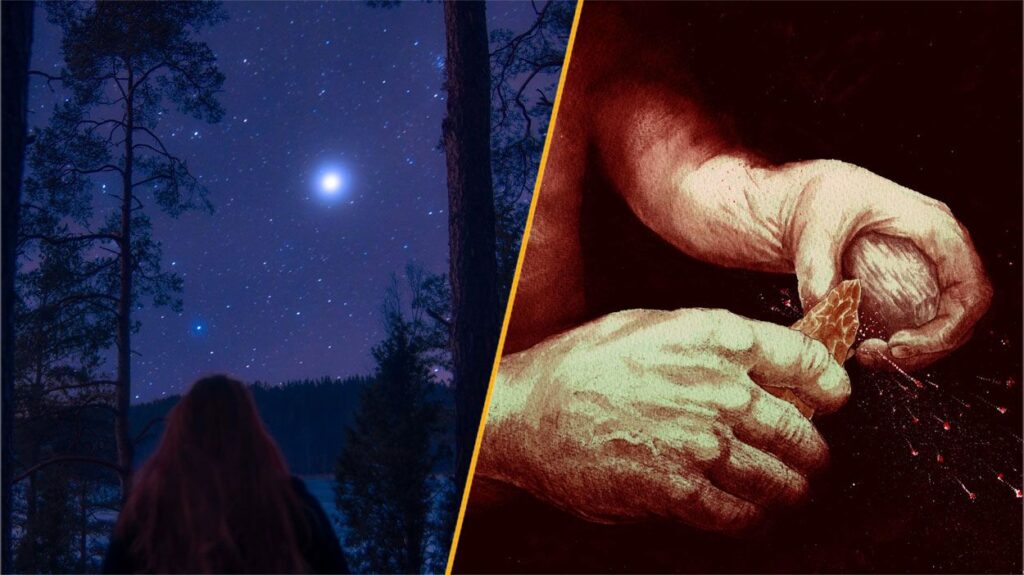
A groundbreaking study has revealed that Neanderthals in England were able to control fire as early as 400,000 years ago. This discovery, made at a site in Suffolk, pushes back previous estimates of when these early humans first harnessed fire by approximately 350,000 years. Researchers found pieces of pyrite, a mineral that can create sparks when struck against flint, at this archaeological site, suggesting that Neanderthals intentionally transported it there to aid in fire-making. The implications of this finding contribute to ongoing debates regarding the social and cultural practices of Neanderthals and their capacity for complex thought.
Animal Behavior: Orcas and Dolphins Team Up
In a remarkable display of cooperation, killer whales off the coast of British Columbia have been observed hunting alongside Pacific white-sided dolphins. A recent study indicates that these two species, typically seen as competitors, exhibit minimal aggression towards each other and even share the spoils of salmon catches. This research is noteworthy as it marks the first documented instance of cooperative hunting and prey-sharing between these marine mammals. However, some experts caution that what appears to be teamwork could also be a form of kleptoparasitism, where one species benefits by stealing food from another.
Exploring Cosmic Phenomena
Turning our gaze to the cosmos, a binary star system known as V Sagittae is expected to become increasingly luminous as it approaches a supernova event within the next century. This stellar phenomenon, characterized by brilliant flares visible to the naked eye, will offer a spectacular view for skywatchers. Additionally, a mysterious X-ray signal detected from deep space may represent the final moments of a star being torn apart by two black holes.
As for our solar system, Jupiter will shine brightly in the night sky this month, prompting speculation about its connection to the biblical Star of Bethlehem. While some enthusiasts may ponder this celestial event, the link remains largely unsubstantiated.
Archaeological Insights from Hadrian’s Wall
Recent excavations at Hadrian’s Wall are reshaping our understanding of life on the fringes of the Roman Empire. This ancient fortification, which marked the northern border of Roman Britain for nearly 300 years, has revealed new insights into the communities that thrived there. Findings from the fort at Vindolanda indicate that the area was not merely a military outpost but rather a vibrant hub of diverse cultures, providing a snapshot of Roman society.
These developments, from the depths of human history to the vastness of space, highlight the ongoing quest for knowledge that drives both scientific inquiry and cultural understanding. As researchers continue to explore these fascinating topics, further revelations are sure to emerge, enriching our comprehension of the world around us.