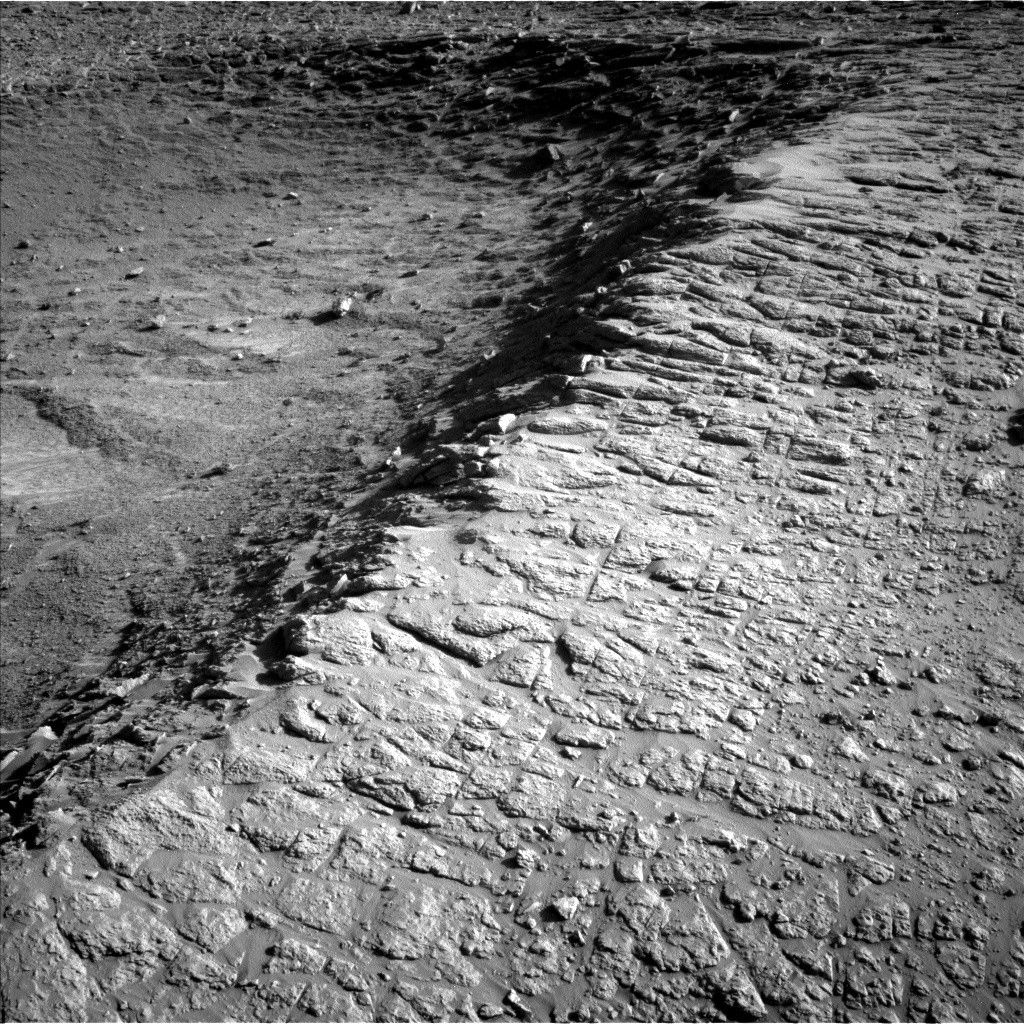
The Curiosity Rover, managed by NASA, recently captured remarkable images while stationed atop a ridge on Mars. On August 21, 2025, the rover documented the view across a geological formation known as the “Thumb,” situated in a topographic depression that scientists plan to explore in the coming days.
Exploration and Imaging Activities
Currently, Curiosity is navigating through intriguing geological structures referred to as boxwork formations, which have been the focus of significant scientific inquiry over the past several months. After departing from the “Río Frío” area, the rover is now positioned on the ridge overlooking the Thumb region. This vantage point provides a unique opportunity to study the surrounding terrain before the rover descends into the depression.
With ample power and three Martian sols available for exploration, the team has outlined an ambitious plan filled with scientific observations. The rover’s Mastcam is set to capture images of several key targets, including “Wallatiri,” “Mojo,” and “Fort Samaipata.” Additionally, the ChemCam instrument will conduct Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) measurements on selected areas, enhancing our understanding of the Martian surface composition.
Among the targets receiving particular attention is Samaipata, which will also be analyzed using the MAHLI camera and the APXS for further elemental analysis. The plan also includes a comprehensive imaging session of the north rim of a nearby crater, utilizing the low dust levels typical of this season to create a detailed 44-image mosaic.
Atmospheric Observations and Future Plans
The scientific activities extend beyond geological studies. Curiosity’s navigation cameras are set to monitor atmospheric phenomena, including dust devils and cloud formations. The rover will also conduct standard atmospheric measurements using the DAN, REMS, and RAD instruments, alongside additional observations to track dust levels.
Despite the packed schedule, the team has decided to conduct a brief drive of approximately 2 meters (about 6.6 feet) to continue their investigation of the ridge. Curiosity remains committed to uncovering the secrets of its Martian surroundings, with further explorations planned for the upcoming sols.
For those interested in following the ongoing journey of the Curiosity Rover, additional updates and detailed findings can be accessed through NASA’s official channels.