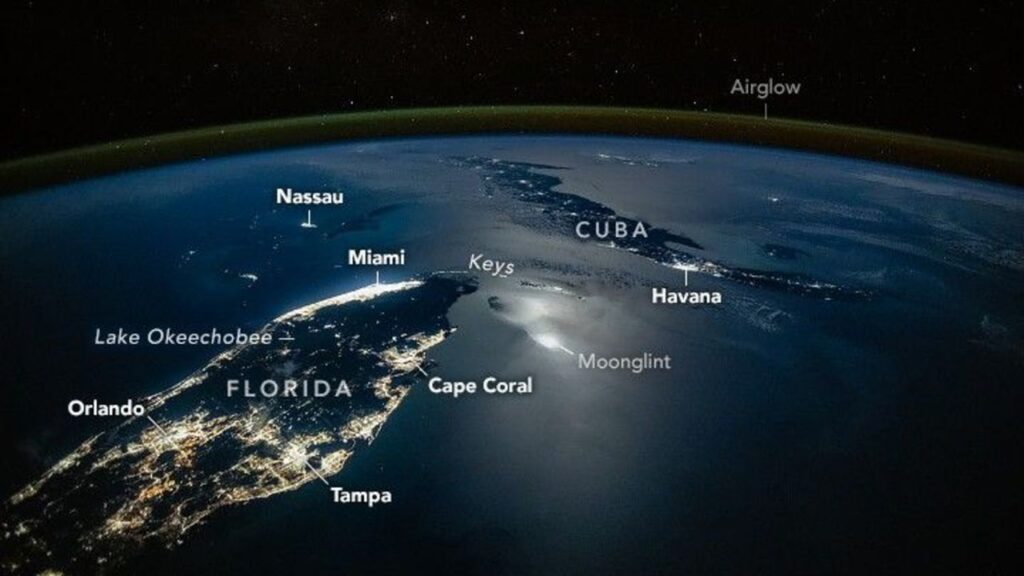
An astronaut aboard the International Space Station (ISS) captured a breathtaking nighttime photograph of Earth on March 19, 2025, showcasing the vibrant lights of Florida and Cuba. The image, taken at 02:23 AM Eastern Time, reveals moonlight glistening over the ocean, with illuminated urban areas highlighting the Florida Peninsula, Caribbean, and parts of Central America.
The photograph features significant population centers, including the bright corridor stretching from Miami to Fort Lauderdale along Florida’s southeastern coast. Other regions such as the Tampa-St. Petersburg area on the Gulf Coast and the Orlando metropolitan zone are also prominently visible. Smaller clusters of light mark the Florida Keys, as well as cities like Havana in Cuba and Nassau in the Bahamas.
Understanding Moonlight Reflections
Aside from the striking city lights, the image is notable for its display of moonglint, which occurs when moonlight reflects off the ocean at the right angle. This phenomenon offers a nighttime counterpart to sunglint, which is seen during the day when sunlight reflects off water. At the time of the photograph, the moon was in a waning phase, approximately 78% illuminated, creating a concentrated reflection across the sea, particularly near the Florida Keys and Cuba.
Captured with a Nikon Z9 digital camera fitted with a 28-millimeter lens, the photo offers a wide field of view akin to that of the human eye. This perspective highlights the curvature of the Earth, accented by a delicate green layer of airglow along the horizon—a reminder of our planet’s atmosphere glowing softly against the vastness of space.
The Importance of Nighttime Earth Observations
Nighttime images like this one reveal intricate patterns of human settlement, infrastructure, and land use that are often difficult to discern during daylight. Scientists utilize such observations to study urban growth, energy consumption, and light pollution, while also examining how human activity interacts with natural environments.
The appearance of moonglint is particularly valuable for researchers. Reflections of moonlight off the ocean can aid in studying sea-surface conditions, such as roughness and wave patterns, even under the cover of darkness. When combined with other data sources, these observations enhance understanding of ocean-atmosphere interactions and refine climate and environmental models.
This photograph not only illustrates the beauty of Earth from above but also serves as a crucial tool for scientific research, shedding light on the impact of human activity on the planet. The image, credited to the NASA/Expedition 72 crew, stands as a testament to the ongoing exploration of our world from the unique vantage point of space.