The widespread use of refrigeration has transformed how we store food, but it may come at a hidden cost. Over-refrigeration can lead to lost nutrients and diminished flavor in fruits and vegetables, raising concerns among health experts and consumers alike.
The Evolution of Food Preservation
Historically, humans have employed various methods to prevent food spoilage, from digging holes in the ground to utilizing cold water in natural bodies. While artificial refrigeration began to take shape in the mid-1700s, it was not until the early 20th century that refrigerators became common household appliances in the United States.
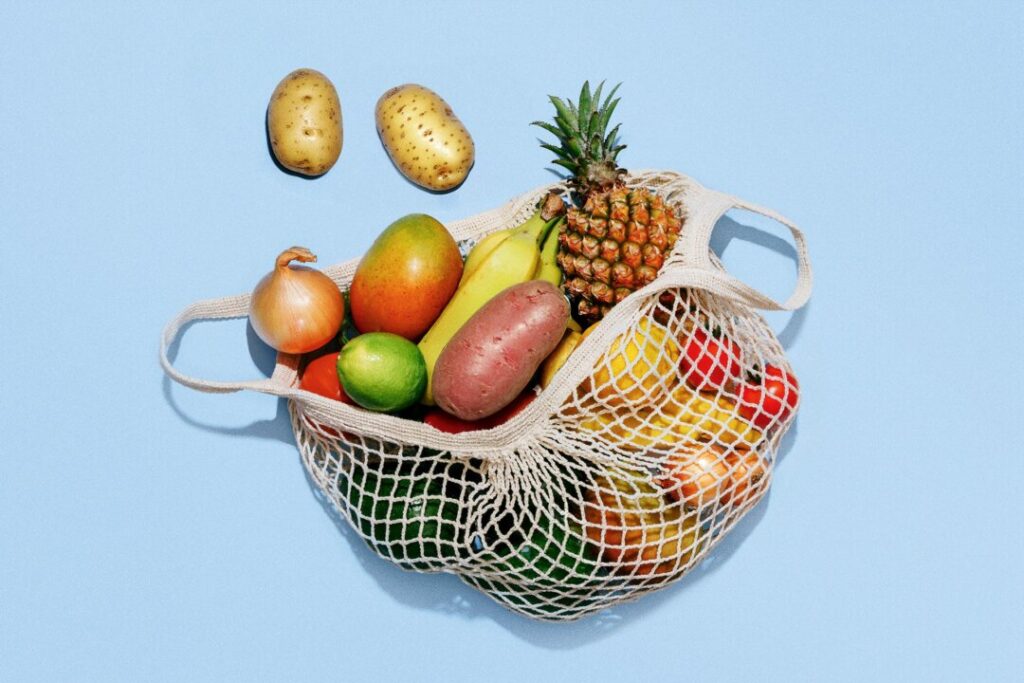
Today, refrigerators are essential in nearly every home, with many people storing a wide array of produce in hopes of maintaining freshness. This practice, however, can result in unintended consequences. Experts have found that certain fruits and vegetables lose vital nutrients and flavor when kept in cold environments for extended periods.
The Nutritional Impact of Cold Storage
Research indicates that refrigeration can impact the nutrient retention of various produce. For instance, vitamin C levels in fruits and vegetables can significantly decline when stored at low temperatures. A study by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) revealed that tomatoes, when refrigerated, can lose up to 50% of their vitamin C content within a week.
Moreover, the cold storage environment can alter the chemical composition of produce, leading to a change in flavor and texture. For example, bananas stored in refrigerators develop a brown peel and mushy texture, rendering them less appealing to consumers. This phenomenon has prompted a reevaluation of best practices for storing fresh produce.
Health professionals emphasize the importance of understanding how different fruits and vegetables react to cold temperatures. The general recommendation is to store items like avocados, bananas, and tomatoes at room temperature to preserve their quality and taste. By doing so, consumers can enjoy produce that is not only more flavorful but also more nutritious.
Additionally, the challenge of over-refrigeration is compounded by consumer behavior. Many shoppers tend to stock their refrigerators to the brim, often leading to extended storage times. As a result, fruits and vegetables may remain unused for longer periods, further diminishing their quality and nutritional value.
As awareness grows regarding the implications of over-refrigeration, some experts advocate for alternative food storage methods. Utilizing breathable storage bags, keeping produce in designated drawers, and regularly checking for spoilage can help maintain the freshness of fruits and vegetables.
While refrigeration has undoubtedly revolutionized food preservation, it is essential to recognize its limitations. By adjusting storage habits and understanding which foods thrive in cold environments, consumers can enhance their culinary experience and promote better health.
Ultimately, the hidden costs of over-refrigeration highlight the need for informed food storage practices. As more individuals educate themselves on the effects of cold storage, they can strike a balance between convenience and quality, ensuring their produce remains as nutritious and flavorful as possible.