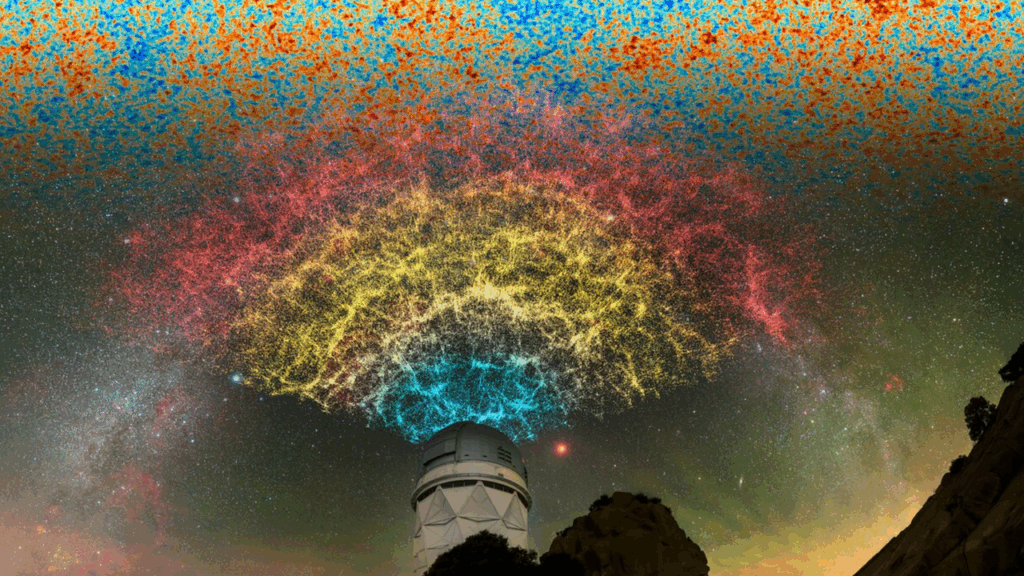
URGENT UPDATE: Astronomers have just revealed that the universe could face its end in a staggering 33 billion years, significantly sooner than previously thought. New insights from the Dark Energy Survey (DES) and the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) indicate that the mysterious force known as dark energy may be evolving, leading to potential catastrophic consequences for the cosmos.
This groundbreaking claim, based on extensive galaxy surveys conducted over the past year, suggests a paradigm shift in our understanding of dark energy. If confirmed, it would challenge the widely accepted cosmological constant model, fundamentally altering our view of the universe’s fate.
The findings propose a complex model involving two key components of dark energy: a hypothetical particle known as an axion and a revised cosmological constant. Researchers emphasize that the axion field is currently driving the accelerated expansion we observe, but this may not last. As axions dissipate, the negative effects of a lower cosmological constant could take over, initiating a slow-down of cosmic expansion and eventually leading to a dramatic Big Crunch scenario.
This theoretical timeline indicates that the universe could enter this collapse phase in as little as 10 billion years. Once this process begins, it will take another 10 billion years to reach a final singularity state. Such a transformation would see galaxies merging and the universe shrinking, marking an end that mirrors the inception of the Big Bang.
The implications of this model are profound. While humanity is currently in a phase of cosmic expansion, the notion that we are over halfway to the universe’s maximum size ignites a sense of urgency about our place within it. The researchers behind this study, presented in June 2023 but not yet peer-reviewed, emphasize that these findings are preliminary and should be approached with caution.
Experts caution that while these observations from DES and DESI are significant, they remain hypotheses. The validity of this model will require further investigation and scrutiny. However, if future studies confirm this trajectory, it could reshape our understanding of the universe’s destiny and humanity’s role within it.
As these developments unfold, the scientific community and the public alike are left to ponder the implications of a universe that may not only be expanding but could also be on the brink of an unprecedented collapse.
Stay tuned for updates as this story continues to develop. The cosmos may hold more surprises in store than we ever imagined.