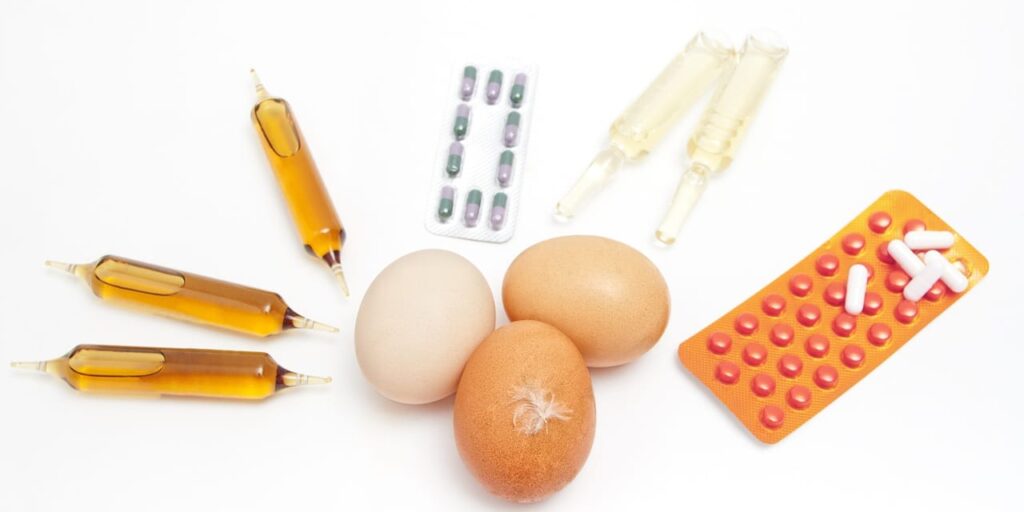
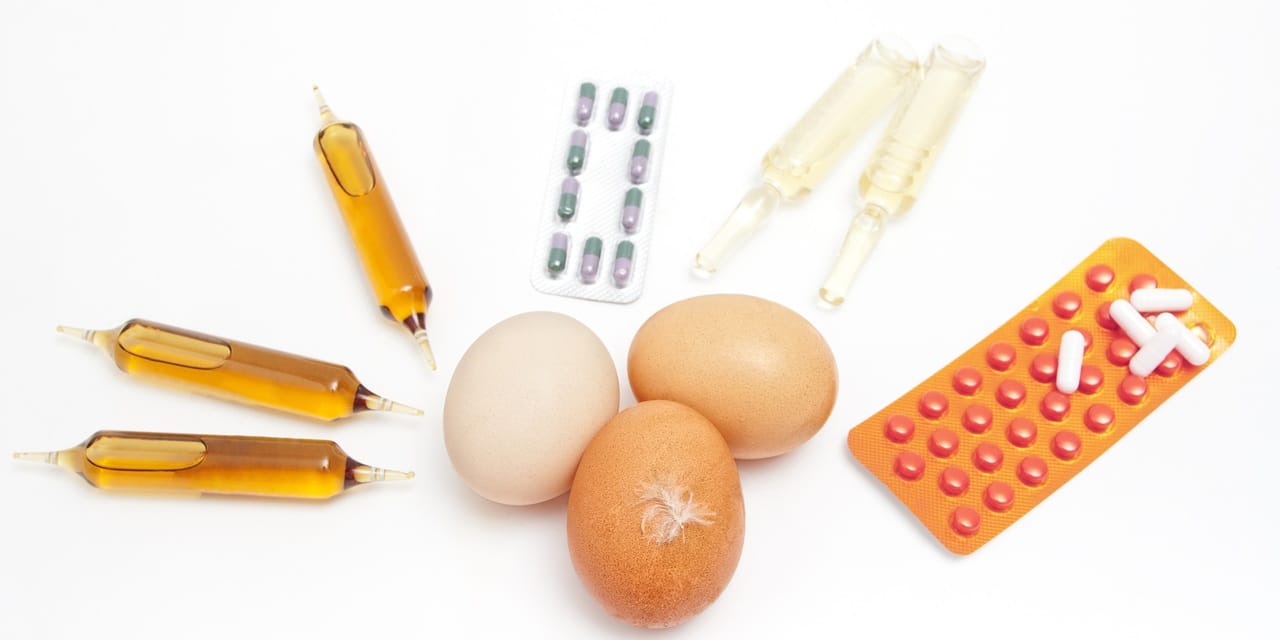
A recent report from the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) indicates a slight rise in the presence of veterinary drug residues in animal products across the European Union. The findings reveal both authorized and banned substances detected in various food items, including meat, dairy products, eggs, and honey.
The report highlights a concerning trend despite a decrease in overall sample testing. In the latest data, the increase in veterinary drug residues reflects potential risks to consumer safety and food quality. The analysis covers substances both permitted for use and those that are prohibited in the EU.
Key Findings and Implications
The findings are based on a comprehensive assessment of food safety conducted by EFSA for the year 2023. Specific data indicates that while the number of samples analyzed has decreased, the rate of detection for residues has slightly increased. This presents a dual challenge for regulatory agencies tasked with ensuring food safety and compliance with EU standards.
Notably, the report pointed out that residues of certain substances, which could pose health risks if consumed, were found in a range of products. The substances identified included both veterinary medicines that are legally permissible and those that are banned for use in food-producing animals.
The implications of these findings are significant. They not only raise questions about the effectiveness of current regulatory measures but also heighten concerns regarding consumer health. As a result, further scrutiny from both government bodies and public health advocates may be anticipated in the coming months.
Future Measures and Consumer Safety
In light of these findings, the EU is expected to review its monitoring processes and enhance regulations to mitigate risks associated with veterinary drug residues. The focus will likely be on increasing testing frequencies and improving protocols for tracking the use of veterinary medicines in food production.
Consumer awareness is another critical component of addressing these issues. The EU encourages transparency in food labeling and will continue to promote educational initiatives regarding safe food practices among producers and consumers alike.
As the EU grapples with these challenges, the need for a robust framework to ensure the safety of food products remains paramount. The efforts to enhance food safety standards will play a crucial role in maintaining public trust in the food supply chain.
With this report serving as a catalyst for action, stakeholders across the food industry will need to address these findings collaboratively to protect consumer health and uphold the integrity of food products in the European market.