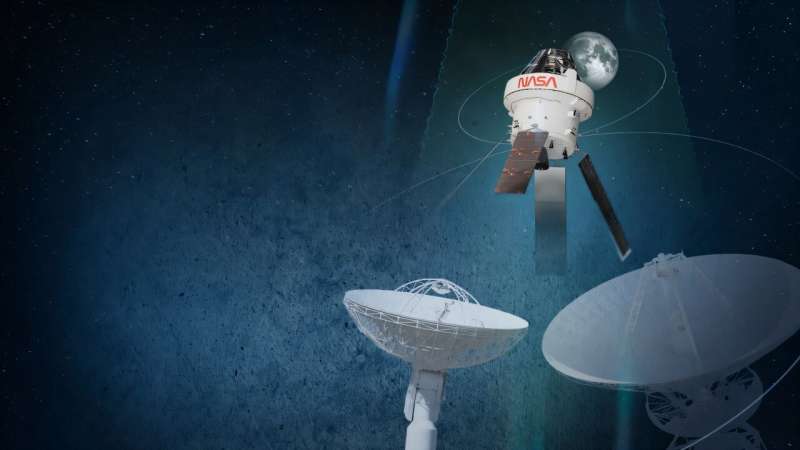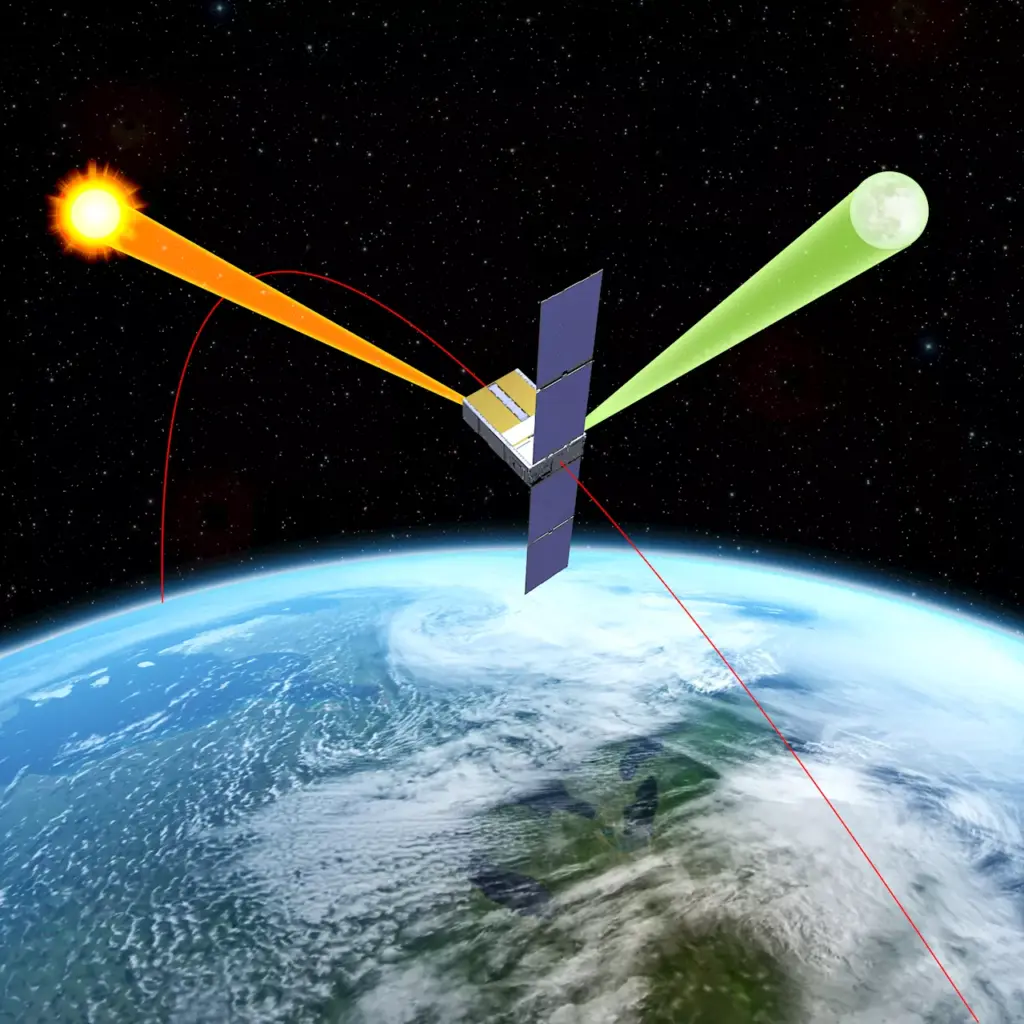
NASA’s innovative Arcstone instrument has successfully completed its primary mission, marking a significant milestone in lunar calibration technology. Launched on June 23, 2023, from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California aboard a SpaceX Transporter-14, Arcstone is now entering its extended operational phase after demonstrating its capabilities.
The primary objective of Arcstone is to enhance the accuracy of lunar calibration for satellite sensors. By measuring light reflected from the Moon, which serves as a stable and precise calibration source, this mission aims to establish a new lunar model vital for Earth-orbiting sensors. These sensors are crucial for various applications, including creating maps used in commercial and scientific endeavors.
Cindy Young, the principal investigator for the mission at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, emphasized the advantages of the instrument’s operational environment. “Since Arcstone is gathering measurements in space, the data it collects does not contain atmospheric effects that increase error, and operations are not dependent on having good weather,” she noted. This capability allows for consistent and frequent lunar sampling, essential for data accuracy.
Arcstone has already achieved notable success, collecting over 240 lunar observations since its launch. The next steps for the science team involve processing and validating the raw data to ensure its precision. This mission is part of a low-cost initiative funded by NASA’s Earth Science Technology Office under the In-space Validation of Earth Science Technologies Program.
The collaboration extends beyond NASA, involving partners such as the University of Colorado Boulder’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics, the U.S. Geological Survey, NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, Resonon Inc., Blue Canyon Technologies, and Quartus Engineering. This diverse partnership underscores the importance of collaborative efforts in advancing space technology and research.
As the Arcstone mission progresses, its findings are expected to play a pivotal role in refining satellite calibration processes. The development of a more accurate lunar model could significantly enhance the quality of data collected by Earth-observing satellites, ultimately benefiting various scientific and commercial applications.
For more information about the Arcstone mission, visit NASA’s dedicated page on the project.