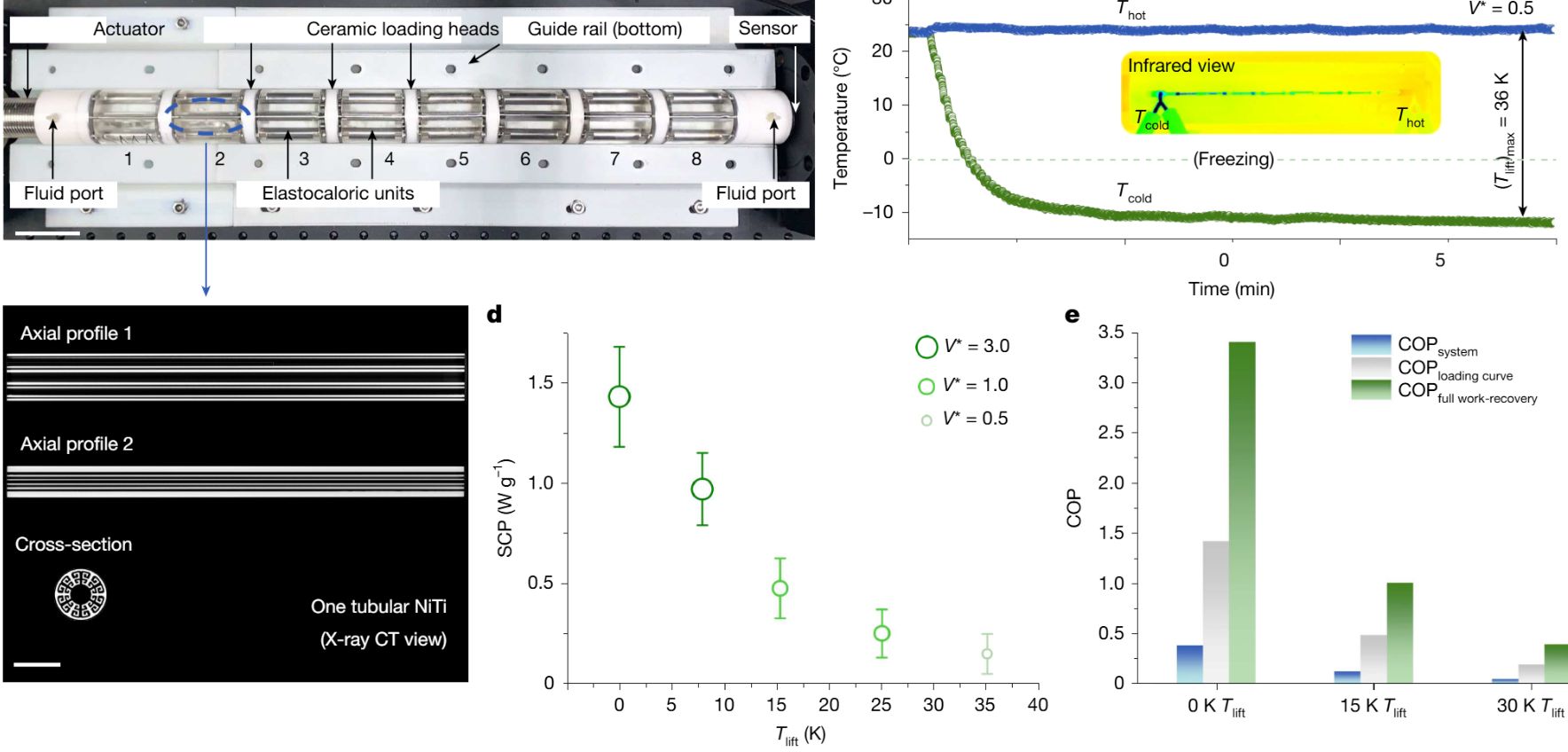
Astronomers have uncovered a dense cocoon of gas surrounding one of the most extreme cosmic explosions ever recorded. Utilizing instruments from the U.S. National Science Foundation National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NSF NRAO), including the Very Large Array (NSF VLA) and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), researchers documented how a powerful black hole tore apart a massive star, subsequently illuminating its surroundings with intense X-rays.
This discovery showcases the capabilities of radio telescopes in studying phenomena that are invisible to traditional optical instruments. The observations reveal that the gas cocoon, which is dense and expansive, plays a crucial role in understanding the aftermath of such cosmic events. The black hole, after consuming the star, generated a shockwave that heated the surrounding gas, resulting in the release of X-ray emissions.
Significance of the Discovery
The findings hold significant implications for astrophysics and our comprehension of black hole activity. The research not only highlights the destructive power of black holes but also emphasizes the complex interactions between these celestial bodies and their environments. By analyzing the gas cocoon, astronomers can gain insights into the processes that govern stellar evolution and black hole formation.
According to the data gathered by NSF NRAO, this event represents a rare opportunity to observe the effects of a black hole’s voracious appetite on its surroundings. The dense gas enveloping the explosion acts as a marker, allowing scientists to trace the black hole’s impact on the interstellar medium. This new information could lead to revised models of black hole behavior and their role in shaping galaxies.
Future Research Directions
The study encourages further exploration using advanced radio telescopes to monitor similar cosmic phenomena. Ongoing and future observations will continue to refine our understanding of these explosive events. The tools available to astronomers today, such as the NSF VLA and ALMA, provide unprecedented detail that enhances our grasp of the universe’s most enigmatic features.
In summary, the discovery of the gas cocoon around this cosmic explosion underscores a pivotal moment in astrophysical research. As scientists delve deeper into the implications of this event, it becomes clear that the universe continues to reveal its mysterious nature, offering new avenues for exploration and understanding. The capacity of radio telescopes to unveil such hidden aspects of the cosmos represents a significant advancement in the field of astronomy.