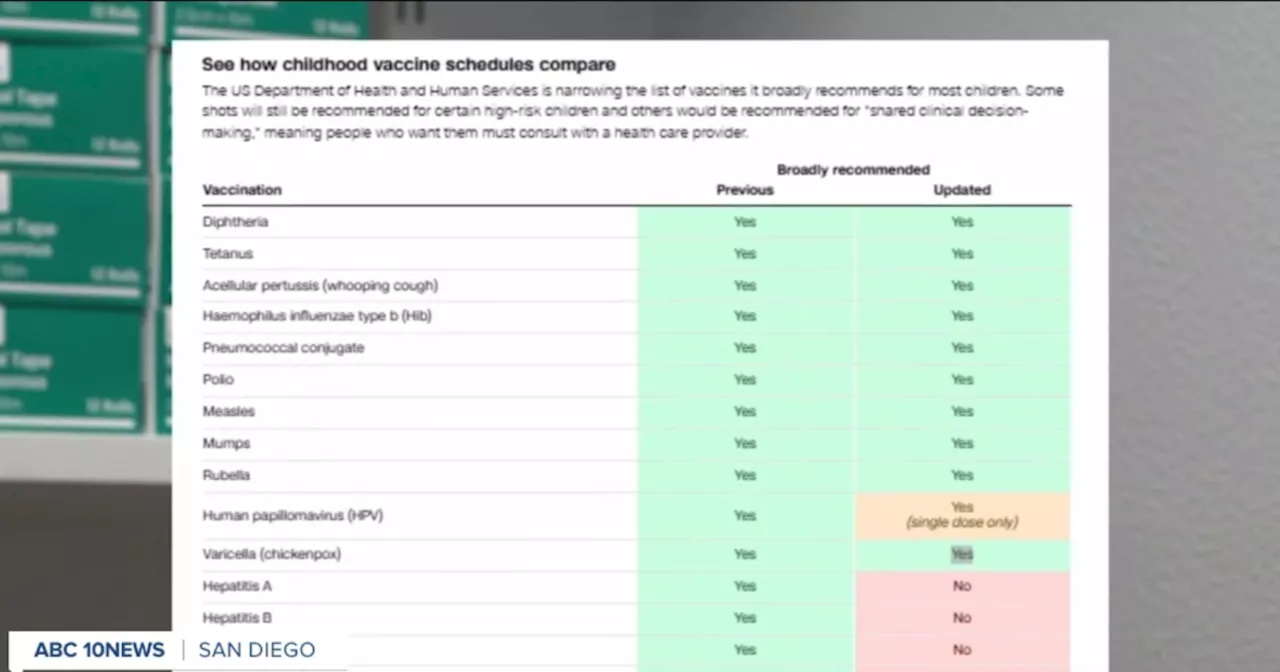
Recent research has shed light on a crucial mechanism that allows the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis (TB) to infect both humans and animals. Scientists discovered that Mycobacterium tuberculosis exploits components of the immune system, which are typically designed to defend against infections, to facilitate its own survival and replication.
The study, conducted by a team at the University of California, reveals that TB’s ability to harness the immune response is a significant factor in its persistence as a global health threat. The findings, published in March 2024, indicate that this manipulation could be key to developing more effective therapies against TB, which affects millions worldwide.
Understanding the precise interactions between Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the immune system can lead to breakthroughs in treatment. TB remains a leading cause of death from infectious diseases, with over 1.5 million fatalities reported annually, according to the World Health Organization (WHO).
Immune Evasion Strategies Uncovered
Researchers focused on how TB interacts with immune cells designed to combat infections. The study shows that the bacterium employs specific mechanisms to evade detection and destruction. By utilizing proteins that mimic those found in host cells, TB can effectively hide from the immune system, allowing it to establish an infection.
This revelation emphasizes the need for new strategies in vaccine development. Current vaccines offer limited protection, suggesting that a deeper understanding of TB’s tactics could pave the way for innovative approaches. As the study elaborates, advancing research in this area is critical, particularly in regions where TB is endemic, such as parts of Africa and Asia.
The team’s findings could also influence public health policies aimed at controlling TB outbreaks. With the economic impact of TB projected to exceed $12 billion in lost productivity each year, addressing this issue is not only a health imperative but also an economic one.
Implications for Future Research
The implications of this research extend beyond immediate health concerns. By elucidating how Mycobacterium tuberculosis manipulates the immune response, the study opens new avenues for research into other infectious diseases that utilize similar evasion strategies.
Researchers are calling for increased funding and resources to further explore these mechanisms. Collaborative efforts between international health organizations and academic institutions could accelerate the development of effective interventions.
The ongoing battle against TB illustrates the complexity of infectious diseases and the constant need for innovation in healthcare strategies. This recent discovery not only deepens our understanding of TB but also reinforces the importance of global cooperation in combating infectious diseases.
As we move forward, the lessons learned from this research may contribute to a more comprehensive approach to tackling TB and possibly other diseases that harness the immune system’s defenses.