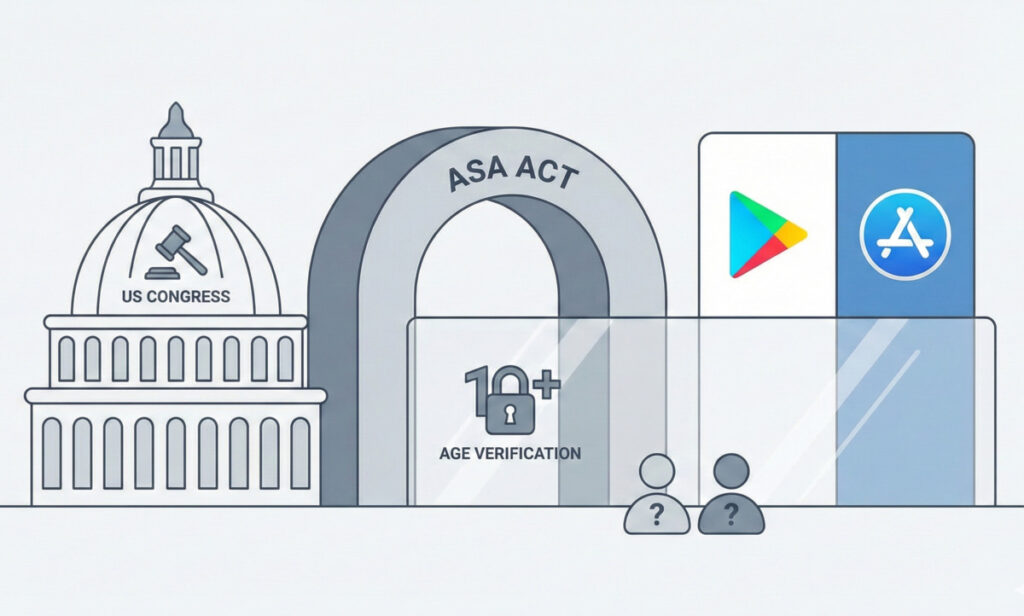
The US Congress is currently debating the App Store Accountability Act (ASA), a legislative proposal aimed at enhancing child safety online through mandatory age verification for app users. This proposed law would shift the primary responsibility for verifying users’ ages from individual app developers to App Store operators, such as Apple and Google. If passed, the ASA would require these companies to implement measures to restrict minors’ access to certain applications while ensuring that user data is handled in a privacy-conscious manner.
Proponents of the ASA, including its sponsors and influential tech companies like Pinterest and Meta, argue that establishing a national standard simplifies the age verification process for parents. They contend that a single federal framework could alleviate the complications arising from the current patchwork of state regulations. By centralizing the responsibility, the burden on individual app developers would also diminish, as they would not need to navigate diverse verification requirements across different jurisdictions.
Despite this support, major tech companies have voiced significant reservations regarding the ASA. Both Apple and Google have expressed concerns primarily focused on privacy issues and the potential for increased liability. They argue that mandating continuous age verification and data sharing could jeopardize minors’ privacy. Additionally, critics of the legislation assert that it effectively shifts responsibility for content moderation from content creators and social media platforms to App Store operators. This shift raises important questions about accountability in the event of a failure to restrict access to harmful content.
Legal challenges are already emerging around such regulatory measures. A similar age verification law implemented in Texas is currently under scrutiny, with critics questioning whether the law infringes upon the First Amendment rights by limiting access to legal content. This backdrop of legal uncertainty complicates the ASA’s potential future, as the debate intensifies over how to balance regulatory objectives with the rights of users.
International Comparisons and Potential Pitfalls
Finding a comprehensive solution to the issue of online safety is proving difficult for lawmakers. The experiences of other countries provide valuable lessons. For instance, the UK’s Online Safety Act sought to limit access to harmful content by enforcing widespread age verification across various platforms. However, the implementation of these measures created significant challenges, leading some websites to block UK users altogether. Moreover, the requirements prompted many individuals to use virtual private networks (VPNs) to circumvent restrictions, ultimately increasing the risk of sensitive data being collected, such as identification documents or credit card information.
The ongoing discussion surrounding the ASA highlights the complexities involved in achieving a balance between regulatory intent and practical application. While the aim of protecting children online is undeniably important, establishing a federal standard that imposes new data-sharing requirements, compromises consumer privacy, and potentially relieves content creators of accountability presents a multifaceted challenge for Congress.
As the debate unfolds, stakeholders from various sectors will be watching closely. The outcome of this legislation could significantly impact the way app stores operate and how user privacy is managed in the digital age, making it a pivotal moment in the conversation around online safety for children.