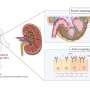
A team of researchers from the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP) in Spain has published a significant review on the potential of extracellular vesicles derived from mesenchymal stem cells in treating kidney injury. The article, which appears in the journal Extracellular Vesicles and Circulating Nucleic Acids, provides an in-depth analysis of how these vesicles can interact with renal tubular epithelial cells, a crucial component in kidney health.
The review highlights emerging evidence that suggests extracellular vesicles may play a therapeutic role in kidney recovery processes. These vesicles, which are small membrane-bound particles released by cells, contain proteins, lipids, and RNA that can influence cellular behavior. The findings point toward a promising avenue for developing treatments for acute kidney injury, a condition that affects millions globally.
Understanding the Mechanism
The research delves into the mechanisms through which mesenchymal stem cell-derived vesicles can affect renal tubular epithelial cells. These vesicles have been shown to communicate with target cells, potentially facilitating repair and regeneration in damaged kidneys. The authors emphasize the need for further studies to fully understand the pathways involved and to establish effective clinical applications.
Given the increasing prevalence of kidney diseases and the limitations of current treatment options, the insights from IGTP researchers could pave the way for innovative therapies. By harnessing the natural regenerative capabilities of stem cell-derived vesicles, medical professionals may soon have new strategies to enhance kidney function and improve patient outcomes.
Broader Implications for Kidney Health
The implications of these findings extend beyond just kidney injury. As researchers continue to investigate the potential of extracellular vesicles, there may be applications in other organ systems and conditions where cellular repair is critical. This research underscores the importance of understanding cellular communication and the therapeutic potential of stem cell technologies in modern medicine.
As the scientific community continues to explore the role of extracellular vesicles, the study from the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute adds valuable insight into a rapidly evolving field. With ongoing research, the hope is to translate these findings into effective treatments that could significantly impact the lives of those suffering from kidney-related ailments.