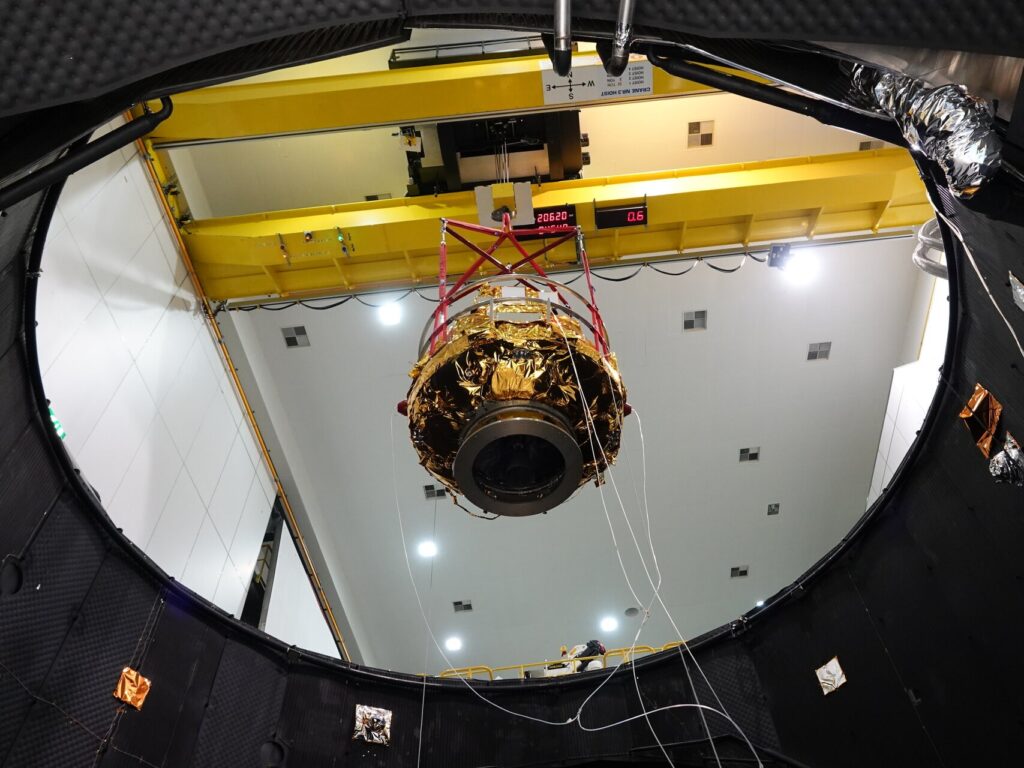
A new mission organized by the European Space Agency (ESA) aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of how Earth responds to solar radiation. The initiative, known as the Solar Orbiter, is set to launch in March 2024 and is expected to greatly enhance our knowledge of solar activity and its effects on the planet.
The Solar Orbiter will explore the Sun’s atmosphere and its magnetic field, generating data that scientists will use to analyze the impact of solar radiation on Earth. This mission holds the potential to deepen our understanding of space weather, which can affect everything from satellite operations to power grid stability.
Scientific Goals and Significance
One of the mission’s critical objectives is to obtain detailed images of the Sun’s poles, a region that has been challenging to study. By observing solar activity from multiple angles, the Solar Orbiter aims to reveal how solar phenomena such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections affect Earth’s atmosphere.
The data collected will not only contribute to scientific knowledge but may also improve predictive models concerning solar weather events. This information is vital for safeguarding technological infrastructure on Earth, particularly in an era where reliance on satellites and electronic systems continues to grow.
International Collaboration and Impact
The Solar Orbiter mission is a collaborative effort involving multiple space agencies, including NASA and ESA. This partnership underscores the importance of international cooperation in addressing global scientific challenges. Researchers from various countries will work together to analyze the data, fostering a shared understanding of solar dynamics.
As the mission unfolds, the findings will likely have implications beyond academia. Enhanced forecasting of solar storms could lead to better preparedness in sectors such as telecommunications, aviation, and energy, ultimately benefiting economies worldwide.
The Solar Orbiter will also help to answer fundamental questions about the Sun’s behavior and its connection to the broader universe. By studying the Sun in greater detail, scientists hope to unravel the mysteries of solar physics and provide insights that could have far-reaching implications for space exploration and our understanding of the cosmos.
With the launch scheduled for March 2024, the scientific community eagerly anticipates the wealth of information that the Solar Orbiter is expected to deliver, marking a significant milestone in the quest to understand Earth’s relationship with the Sun.