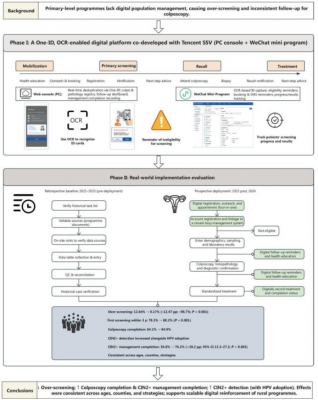
Cervical cancer continues to be a significant health threat, particularly in resource-limited rural areas, contributing to high rates of preventable deaths among women. In response to this issue, researchers have assessed a digital platform known as “One-ID,” developed by the Tencent Inclusive Health Lab. This innovative tool utilizes optical character recognition (OCR) technology to enhance population-based cervical cancer screening.
The One-ID platform is designed to streamline the screening process, making it more efficient and accessible. By integrating OCR technology, health care providers can improve the accuracy of data collection and analysis. This advancement is crucial, especially in regions where access to medical professionals and diagnostic tools is limited. The platform aims to reduce unnecessary procedures while improving the overall detection rate of cervical cancer.
According to the research findings, the implementation of the One-ID platform has led to a marked decrease in the overuse of medical resources. By focusing on accurate data processing, the platform allows healthcare workers to prioritize patients who require immediate attention. This targeted approach not only optimizes resource allocation but also enhances patient outcomes.
The challenges of cervical cancer screening are particularly pronounced in rural settings, where logistical difficulties can hinder effective health interventions. The One-ID platform addresses these challenges by simplifying the information-gathering process, thus enabling healthcare workers to respond more effectively to the needs of their communities.
Impact on Women’s Health
The implications for women’s health are substantial. Cervical cancer screening is vital for early detection, which significantly increases the chances of successful treatment. By improving screening procedures, the One-ID platform could lead to a decrease in cervical cancer mortality rates, particularly in underserved populations.
Health experts emphasize the importance of accessible screening methods. Dr. Li Wei, a researcher involved in the study, noted, “The One-ID platform represents a significant leap forward in cervical cancer screening. By leveraging technology, we can reach more women and ensure they receive the care they deserve.”
As the research continues, the potential for broader implementation of the One-ID platform in various healthcare settings remains a priority. The goal is to establish a scalable model that can be adapted to different regions, thereby maximizing its impact on public health.
In conclusion, the integration of AI technology into cervical cancer screening holds promise for improving healthcare outcomes. As researchers continue to evaluate the effectiveness of the One-ID platform, the hope is to create a sustainable framework that can save lives and promote health equity for women in both urban and rural communities.







