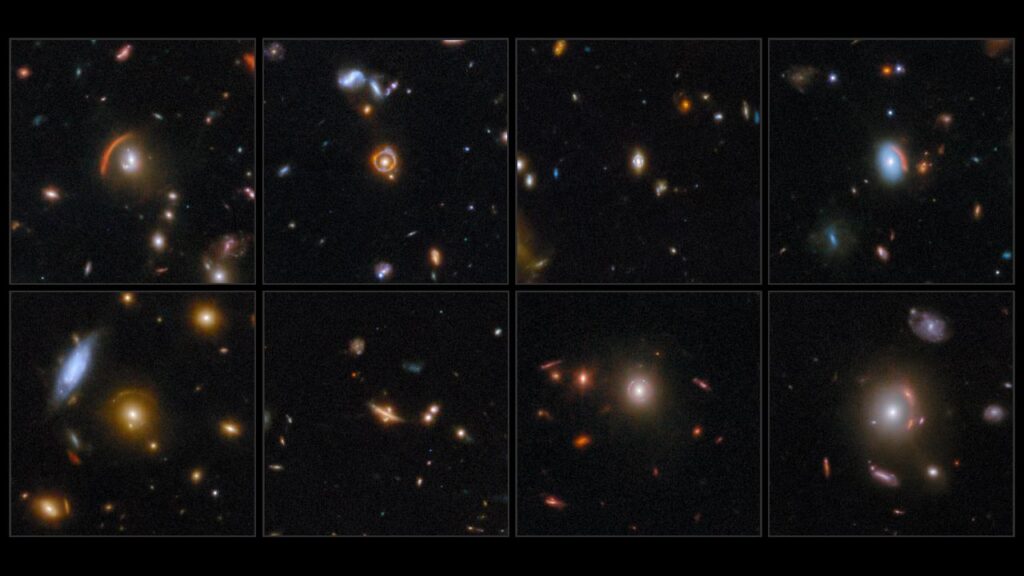
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has made a remarkable discovery by capturing images of eight distinct “Einstein rings,” a phenomenon that validates Albert Einstein‘s predictions about gravitational lensing. This significant achievement was announced on September 30, 2025, showcasing the telescope’s ability to peer into the depths of the universe and reveal intricate cosmic structures.
Gravitational lensing occurs when massive objects, like galaxies, bend the fabric of space-time around them. This bending causes light from more distant galaxies to warp, creating arcs or complete rings. The eight galaxies imaged by JWST exhibit these remarkable shapes, providing a natural magnification of celestial objects that would otherwise remain hidden from our view. The images are not mere optical illusions; they exemplify a phenomenon first predicted by Einstein over a century ago.
Insights from the COSMOS-Web Project
These extraordinary images result from the COSMOS-Web project, one of the largest observational programs conducted with the JWST. Over the course of 255 hours, scientists targeted more than 42,000 galaxies, identifying over 400 potential examples of Einstein rings. Among the most striking is the image of COSJ100024+015334, a perfect ring that reflects a galaxy as it existed just one billion years after the Big Bang, highlighting its youth compared to the universe’s current estimated age of over 13 billion years.
While some of these galaxies have been observed previously by the Hubble Space Telescope, JWST’s advanced infrared capabilities provide a clearer view, uncovering details that were previously obscured by dust and distance. This leap in imaging technology allows astronomers to gain deeper insights into the structure and formation of galaxies.
Impact on Astronomical Research
The phenomenon of gravitational lensing not only enhances our view of distant galaxies but also enables scientists to study the mass of these galaxies, including the elusive dark matter that remains invisible to conventional measurement methods. The rare alignments that produce Einstein rings create opportunities for researchers to explore the fundamental building blocks of galaxies, star clusters, and even supernovae.
This research is crucial for understanding how galaxies formed and evolved in the early universe. By examining these cosmic structures, astronomers can glean insights into the influence of dark matter on the cosmos during its formative years. The JWST’s findings exemplify the telescope’s potential to revolutionize our understanding of the universe.
With each new image and discovery, the James Webb Space Telescope continues to unlock the cosmos, offering humanity a glimpse into the vast and enigmatic universe that surrounds us. These stunning captures are a testament to the power of modern astronomy and the collaborative efforts of scientists worldwide. As this research progresses, it promises to deepen our understanding of our place in the universe and the fundamental forces that govern it.