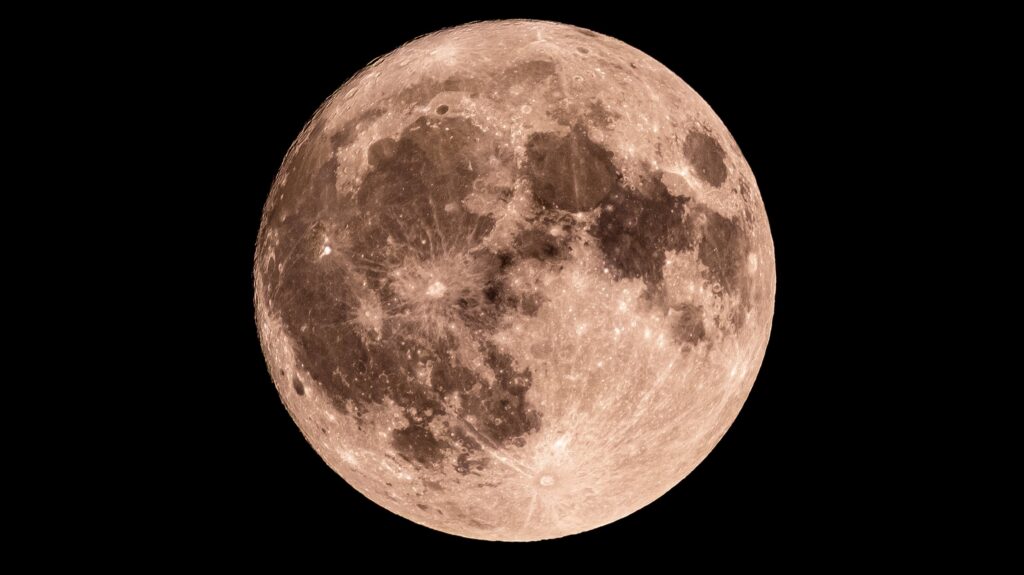
The night of September 6, 2025, will showcase a striking Waxing Gibbous Moon, with approximately 98% of its surface illuminated. This lunar phase occurs as part of a cycle that spans about 29.5 days, during which the Moon’s visibility changes due to its orbit around Earth, according to NASA.
As the Moon rises tonight, it will be an excellent opportunity for stargazers to explore its surface. With the naked eye, viewers can spot prominent features such as the Mare Imbrium, Mare Vaporum, and Mare Fecunditatis. For those equipped with binoculars, the Grimaldi Basin and Gassendi Crater become visible, while telescope users can enjoy detailed views of the Apollo 14 and 17 landing sites, along with the Rupes Altai.
Understanding the Moon Phases
Moon phases are a result of the changing angles between the Sun, Moon, and Earth during the lunar orbit. As the Moon travels around Earth, the portion that is illuminated by sunlight shifts, creating a series of distinct phases. The primary phases include:
– **New Moon**: The Moon is positioned between Earth and the Sun, making it invisible from our perspective.
– **Waxing Crescent**: A small portion of the Moon begins to light up on the right side.
– **First Quarter**: Half of the Moon appears illuminated on the right side, resembling a half-moon.
– **Waxing Gibbous**: More than half of the Moon’s surface is lit, but it has not yet reached full illumination.
– **Full Moon**: The entire face of the Moon is illuminated and fully visible.
– **Waning Gibbous**: The illuminated portion begins to decrease on the right side.
– **Last Quarter** (or Third Quarter): The left side becomes lit, appearing again as a half-moon.
– **Waning Crescent**: A thin sliver of light remains on the left side before the Moon returns to darkness.
The upcoming full moon will take place on September 7, following the last full moon on August 9.
Understanding the lunar cycle not only enhances the appreciation of our natural satellite but also connects us to the rhythms of nature. As the Waxing Gibbous Moon illuminates the night sky, it serves as a reminder of the celestial wonders that can be explored.