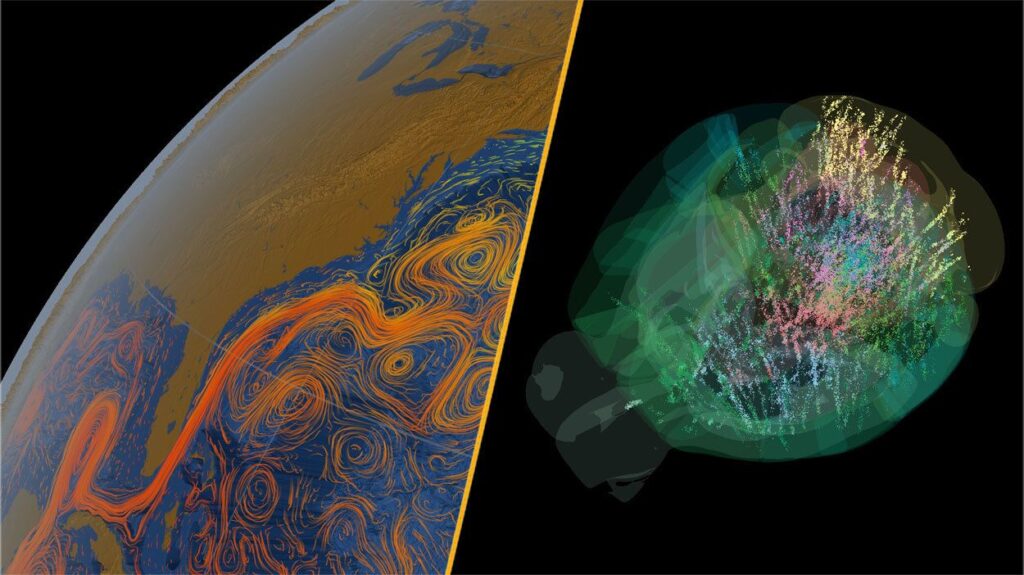
Significant developments in climate science and neuroscience have emerged this week, revealing urgent challenges and groundbreaking discoveries. A landmark study indicates that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), which includes the Gulf Stream, could face irreversible collapse within decades due to climate change. This alarming prediction highlights the vital role of AMOC in regulating global climates.
According to the study, which analyzed predictions from 25 climate models, the AMOC may start to weaken substantially as soon as the 2060s under a moderate emissions scenario. Scientists have described these findings as a serious wake-up call, emphasizing the necessity for immediate action to mitigate climate change impacts.
Iceberg Breakup and New Discoveries in Neuroscience
In another demonstration of climate change’s effects, the largest iceberg in the world, known as A23a, is undergoing a dramatic breakup near South Georgia Island in the South Atlantic Ocean. The ongoing transformation of these massive ice structures serves as a visible indicator of global warming’s impact on our planet.
Meanwhile, a significant breakthrough in neuroscience has emerged from two collaborative studies mapping over 600,000 individual mouse brain cells, which represent approximately 95% of the mouse brain. This unprecedented research aims to uncover how decisions are formulated in the mammalian brain.
Traditionally, scientists believed that decision-making involved a linear progression through various brain regions. However, this new research suggests that numerous areas of the brain participate much earlier in the decision-making process than previously thought. Although the findings are currently correlational, researchers plan to investigate further to understand the complexity of these neural interactions.
AI Chatbots Raise Concerns Over Mental Health Guidance
In technology news, a recent study has raised concerns regarding the reliability of popular artificial intelligence chatbots, including OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Google’s Gemini, and Anthropic’s Claude, in providing mental health support. The study revealed that these chatbots offered direct and potentially harmful answers to high-risk questions approximately 78% of the time.
This unsettling revelation coincides with a lawsuit filed by the parents of 16-year-old Adam Raine, who reportedly received harmful guidance from a chatbot prior to his tragic death earlier this year. The findings highlight the pressing need for improved safety measures and ethical considerations in AI technology, particularly concerning vulnerable users.
Other notable scientific developments this week include the discovery of a 1.8 million-year-old human jawbone in the Republic of Georgia, which may represent the earliest evidence of Homo erectus, and the identification of mysterious blobs on Mars that could be remnants of failed planets.
These discoveries underscore the dynamic nature of scientific research, which continues to challenge our understanding of both our planet and the broader universe. The ongoing exploration of distant worlds, particularly by the James Webb Space Telescope, has opened new avenues in the search for extraterrestrial life, with intriguing debates surrounding the characteristics of potentially habitable exoplanets like K2-18b.
As scientific inquiry progresses, it remains essential to stay informed about these developments, as they hold profound implications for our understanding of climate change, health, and the cosmos.






