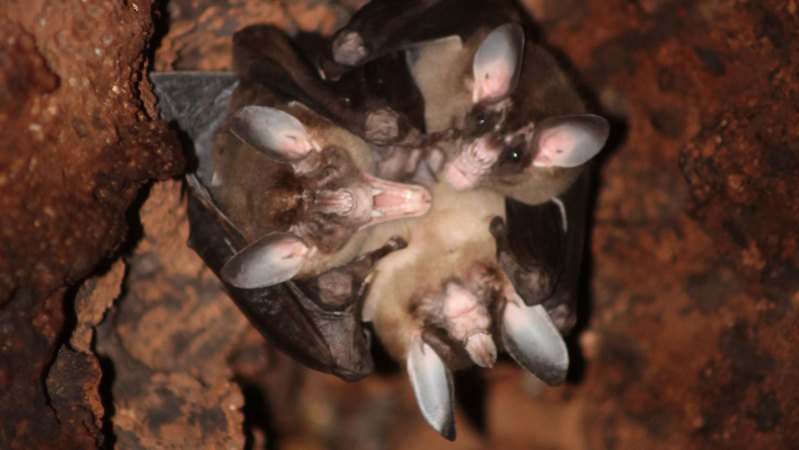
Recent observations in Costa Rica have unveiled remarkable social behaviors among the world’s largest carnivorous bats. Utilizing infrared cameras, researchers discovered that these bats engage in affectionate actions such as hugging and cuddling, as well as sharing their meals with one another.
The study, conducted by a team of biologists, highlights the complex social structures these bats maintain. The **giant carnivorous bat**, known scientifically as *Desmodus rotundus*, has been shown to exhibit behaviors that suggest strong social bonds among individuals. The infrared cameras captured footage of bats wrapping their wings around each other, a behavior indicative of close relationships.
This groundbreaking research underscores the importance of social interactions in the animal kingdom. The bats not only demonstrate physical affection but also actively engage in sharing food, which is particularly significant for a carnivorous species. Sharing meals among these bats can enhance their social ties and improve their chances of survival in the wild.
Social Bonds Through Affectionate Behaviors
The affectionate behaviors observed were not just casual; they indicate a deeper level of social connectivity. The researchers noted that the wing wraps often occurred between bats that had previously shared meals. This suggests that the act of sharing prey reinforces relationships and fosters a sense of community among these creatures.
The implications of these findings extend beyond mere curiosity. Understanding the social dynamics of the **giant carnivorous bat** can provide insights into their behavior and ecology, which are vital for conservation efforts. With habitat loss and climate change threatening their populations, recognizing the importance of social structures could inform strategies to protect them.
The infrared cameras used in the study allowed researchers to monitor the bats’ behaviors without disturbing their natural environment. This method has proven effective in capturing behaviors that might otherwise go unnoticed, revealing a richer tapestry of animal life.
Implications for Conservation and Research
The research emphasizes the necessity of further investigation into the social lives of bats and other wildlife. As scientists continue to study these behaviors, they can better understand how social bonds influence survival and reproduction in species that are often misunderstood.
In addition to shedding light on the **giant carnivorous bat**, the findings could have broader implications for the study of social behaviors in other animal species. Understanding the nuances of animal interactions can enhance conservation efforts and contribute to the preservation of biodiversity.
As the world grapples with environmental challenges, recognizing the intricate social lives of creatures like the **giant carnivorous bat** may play a crucial role in ensuring their survival. The research not only highlights their affectionate behaviors but also reinforces the need for a more profound respect for the complexities of wildlife.
Overall, the study provides a compelling look at the social behaviors of the **giant carnivorous bat**, emphasizing the importance of community and connection in the animal kingdom. It serves as a reminder that every species plays a vital role in our ecosystem, and protecting their social structures is essential for their continued existence.